Avoid Insurance Claims: Grilling Accidents Cause Nearly 10,000 Fires Annually

Few things say summer like firing up the grill. But with that sizzle comes a surprising amount of risk. According to the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), grill-related fires spike during summer months.
July accounts for 15% of all grill fires, followed closely by June (14%), May (13%), and August (12%).
Grilling accidents cause an average of $37 million in property damage per year. On top of home damage, grill-related injuries send roughly 21,682 people to the emergency room every year.
These incidents are often the result of malfunctioning equipment, which homeowners can address through routine checks or maintenance. Below, we’ll walk through straightforward, actionable steps to help reduce your risk of grill-related fires, helping safeguard your home and avoid preventable fire insurance claims.
Common causes of grilling accidents
Improper cleaning practices and maintenance
Faulty grilling equipment and bad grill placement
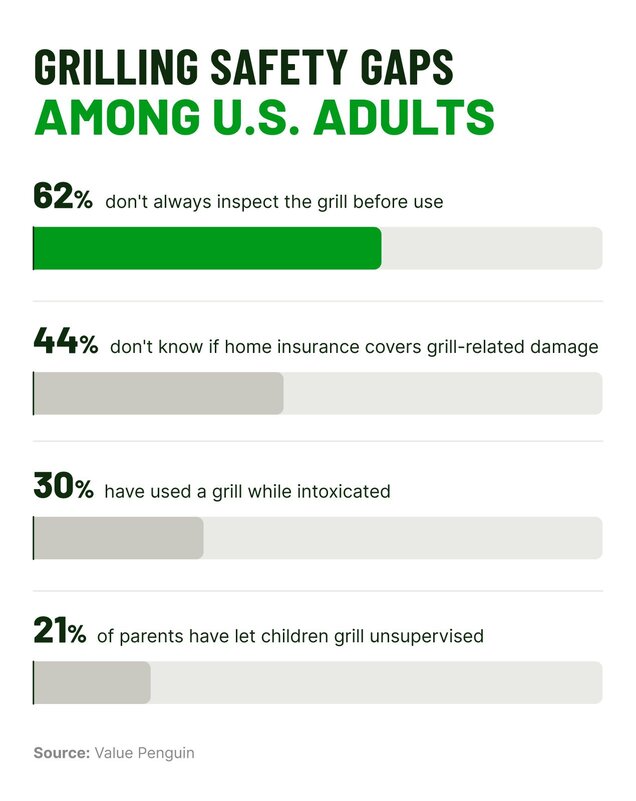
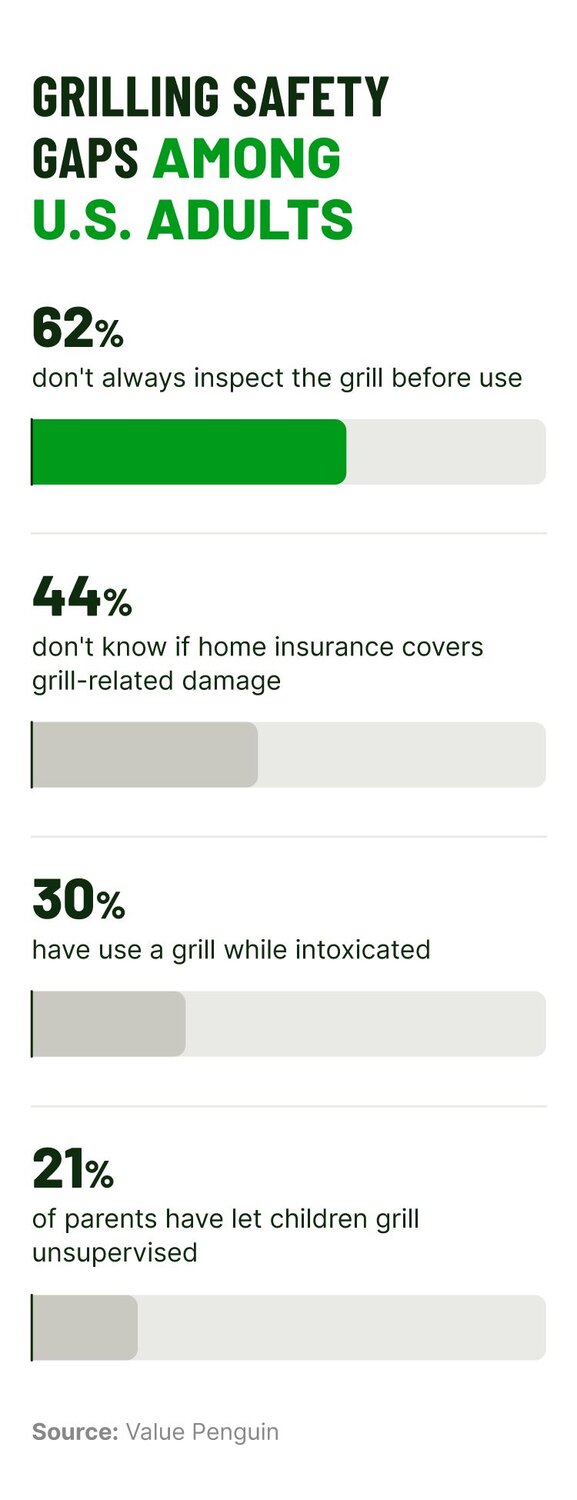
Irresponsible or impaired use
Grill safety tips to help prevent housefires
- Review your home insurance coverage to ensure your policy offers adequate protection. Check out typical home insurance coverage to understand any potential limitations.
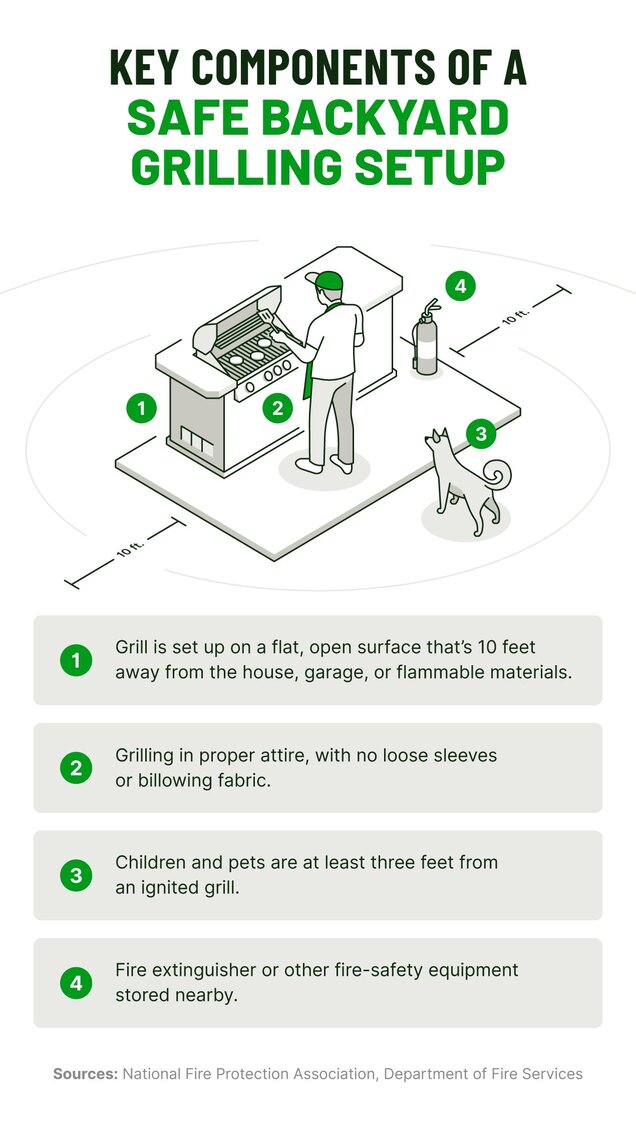
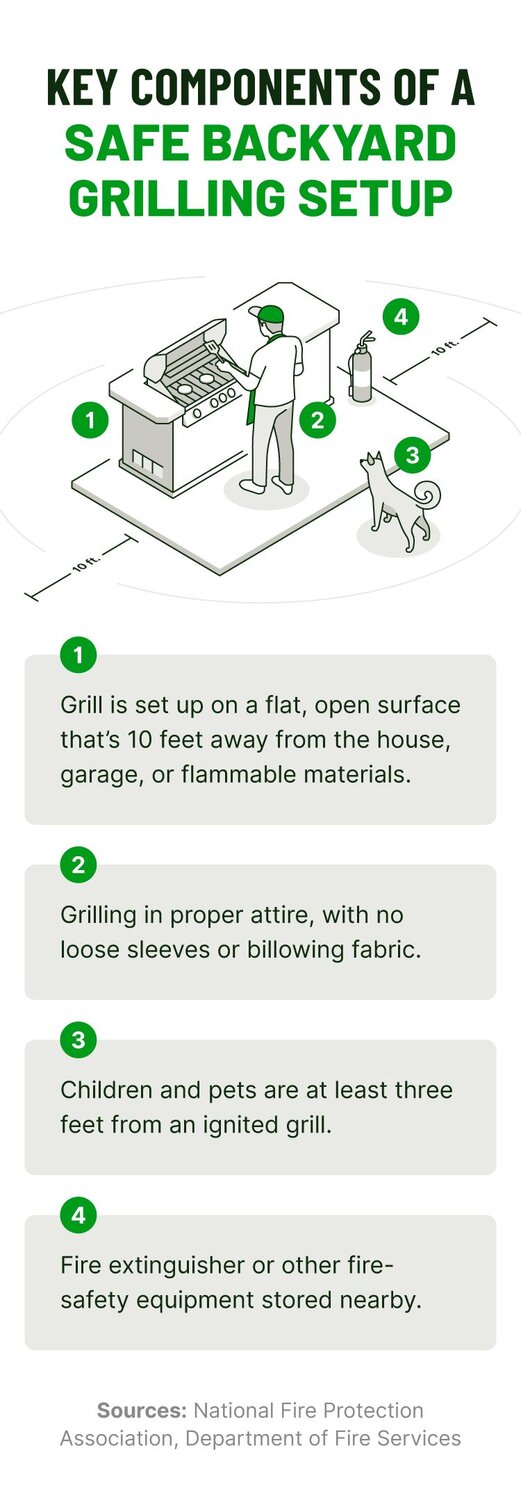
- Keep a fire extinguisher or other fire-safety equipment nearby in case of a fire. Make sure you know how to use these tools before you need them.
- Never leave a grill unattended while using it. Fires only take seconds to ignite.
- Regularly clean your entire grill, not just the grates. Proper cleaning can help reduce the risk of flare-ups and keep your equipment working more efficiently.
- Set up your grill on a flat, open surface that’s at least 10 feet away from your house, garage, or any flammable structures.
- Carefully inspect your grill before each use. Look for worn parts, test for leaks using soapy water on hose connections, and replace any damaged components right away.
- Never let children grill unsupervised. The NFPA recommends keeping kids and pets at least three feet away from grills while they’re in use.
- When grilling, wear clothing that won’t easily ignite. Avoid loose sleeves or billowing fabric.
- Be cautious when using fire starters, like charcoal starter fluid. Only use the proper solutions designed for your grill type, avoiding charcoal fluid or other flammable liquids.
What to do if a grill fire damages your home
- Call emergency services immediately: Even if the fire seems manageable, it’s important to have professionals assess the situation. Fires can spread quickly and may cause hidden damage.
- Ensure everyone's safety: Get people away from the area and ensure no one re-enters the space until it’s declared safe.
- Stop the spread—safely: If it’s safe, use a fire extinguisher rated for grease fires. Never use water, as it can make grease fires worse.
- Document the damage: Once the fire is out, take detailed photos and videos of all affected areas. Include both exterior and interior damage.
- Review your coverage: Nearly 4 in 10 grill owners say they don’t know whether their policy covers fire damage. If you're unsure what your policy includes, take a moment to understand the different types of homeowners insurance and when it typically applies.
- Contact your insurance provider: Report the incident and quickly file your home insurance claim. Having any related documentation ready will help streamline the process.
Identifying the safest grill type for your home
Higher risk: Gas grills
If you choose a gas grill, check for leaks, store propane tanks properly, and keep the grill clean and well-maintained.
Medium risk: Charcoal grills
Let the ashes in a charcoal grill cool completely and dispose of them in a metal container.
Lower risk: Electric grills
Plugging an electric grill directly into a grounded outlet—not an extension cord—can potentially decrease the risk of fire.
Tips to find the right grill for your home
- Space and environment: Electric grills are good options for small outdoor spaces, especially where open flames are restricted. Charcoal and gas grills require more ventilation and should be farther from structures and overhangs.
- Safety comfort level: Choose a grill you feel confident operating and maintaining. Gas grills require more frequent inspection and upkeep, while electric models are generally lower maintenance.
- Insurance coverage: Review your homeowners insurance to understand what's covered if a grill-related fire occurs. Some policies may have exclusions or limits, so it’s important to check those details.
- Local regulations: Some cities, condos, and HOAs restrict charcoal or gas grills. Always check your local rules before buying a grill.
- Portability and storage: Smaller electric or compact gas grills may be better if you plan to move the grill frequently or have limited storage space.
Take grill safety seriously and know your coverage options
Download the safe grilling checklist
Related Articles

How To Fireproof Your Home + Fire Safety Checklist

Survey: 66% of Homeowners Experience Summer Plumbing Issues

11 Pool Safety Tips for a Worry-Free Summer [Free Checklist]

27 U.S. House Fire Statistics + Tips to Help Protect Your Home [2024]

How To Save on Your Electric Bill: 10 DIY-Able Ways To Save This Summer

